Filter and sort
What is a solar optimizer and what is it used for?
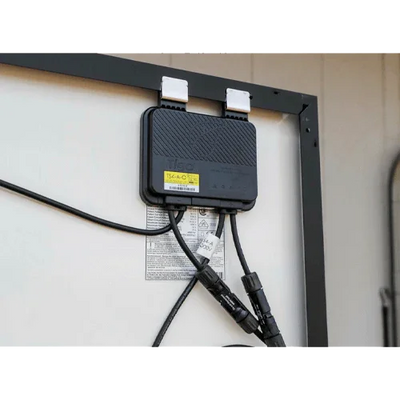
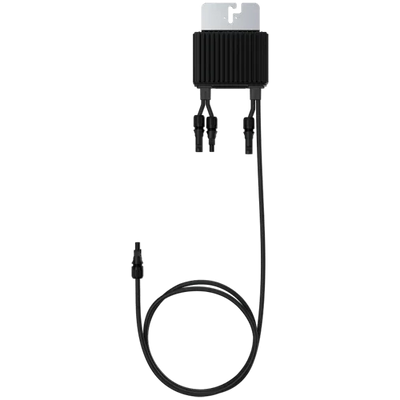
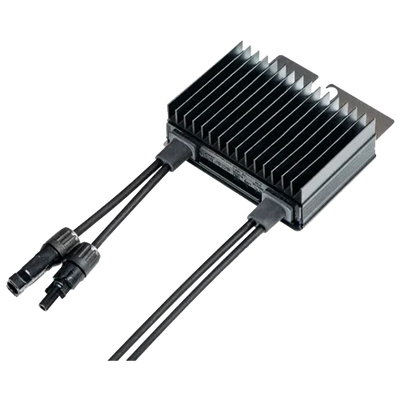
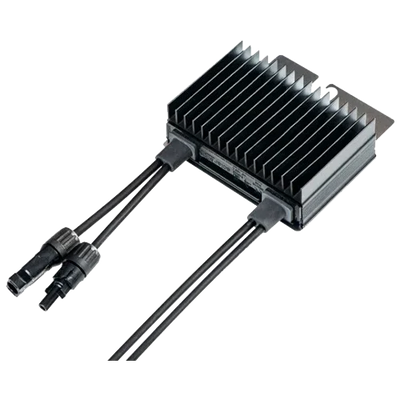
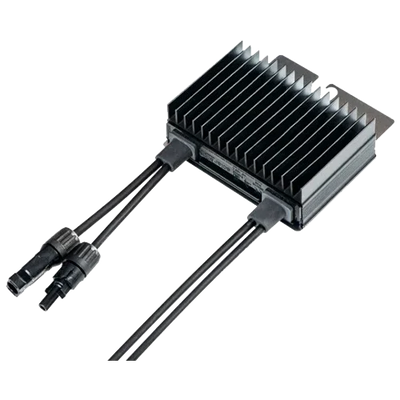
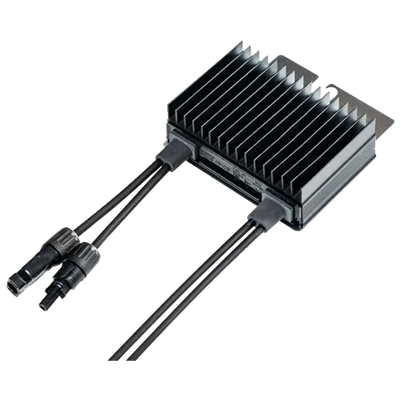
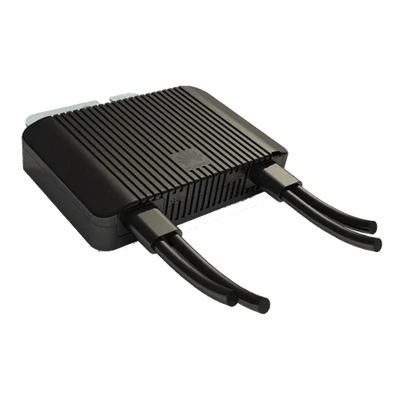
A solar optimizer is a DC-DC converter that works in conjunction with the photovoltaic module or a small set of modules. Its function is to electrically decouple the panels from each other so that a shadow or a mismatch (power tolerances, dirt, aging) does not drag down the production of the entire string. This improves local maximum power point tracking (MPPT), provides granular monitoring, and enables safety functions such as rapid DC shutdown.
Advantages
- More kWh on roofs with partial shading, different orientations, or mixed modules.
- Module-level monitoring to detect abnormal performance, dirt, or failures.
- Safety with DC voltage reduction for maintenance or emergency (depending on the system).
- Design flexibility: longer strings or combinations of tilts/azimuths with lower losses.
Limitations
- They do not replace good design: avoid fixed shading if possible and respect inverter limits.
- They add electronics on the roof; confirm thermal dissipation and connector compatibility.
- The gain depends on the shading profile and the percentage of affected modules.
Recommended applications
- Residential roofs with chimneys, dormers, skylights, or nearby trees.
- Installations with dual-pitch or east-west orientation in the same field.
- Projects requiring detailed diagnostics and data-driven maintenance.
How to choose a solar optimizer
- Maximum admissible power (Wp/W): must cover the module's STC power with margin.
- Input voltage (Voc max.): ensure that the Voc at minimum temperature does not exceed the limit.
- Input current (Isc max.): choose a model that supports the panel's Isc with thermal margin.
- Compatibility: verify integration with your inverter (proprietary or universal brands/systems).
- Environment: temperature range, IP rating, and connector type (MC4/compatible).
Typical specifications (indicative)
| Admissible module power | Up to 400–700 Wp per optimizer (depending on model) |
| Max. input Voc | ≈ 60–125 V per module |
| Max. input Isc | ≈ 12–15 A |
| Efficiency | ≥ 98% (DC-DC converter) |
| Protection | IP65–IP68; rapid DC shutdown (depending on system) |
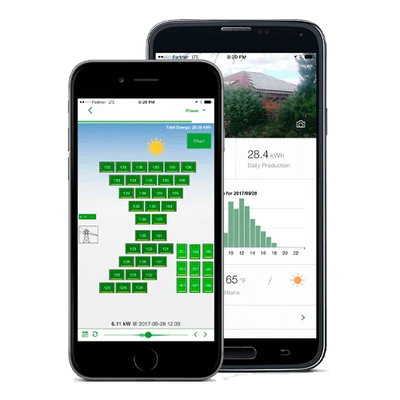
| Monitoring | Per module or per string, via app/portal |
Always check the manufacturer's datasheet: admissible power, maximum Voc and Isc must match or exceed those of the module under your site's conditions.
Best practices
- Model seasonal shading to size the number of optimizers needed.
- Leave a safety margin in Voc at minimum temperature and in Isc at high irradiance.
- Manage cabling and ventilation under the module; avoid loops and check connector torque.
- Integrate DC protections (fuses, disconnect switch, and SPD) according to the inverter diagram and applicable regulations.
Comparisons and related collections
If your priority is to maximize production with limited space, combine optimizers with Monocrystalline Panels. For ground-mounted projects or light-colored roofs where albedo is high, see Bifacial Panels. For bulk purchases and batch uniformity, consult Packs and Pallets. Complete the installation with Solar Panel Accessories (cables, MC4 connectors, clamps, and protections).
Related accessories
- Solar Panel Accessories (solar cable, connectors, fixings, and SPD).
- Monocrystalline Panels and Bifacial compatible by power and current.
Solar Optimizers provide performance, visibility, and safety in real-world scenarios with shading or mismatches, helping to stabilize production and get the most out of each installed module.