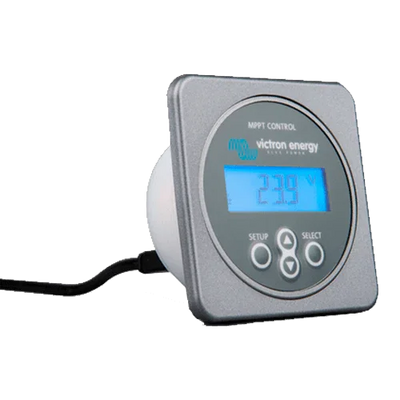
Filter and sort
When to choose a 24V inverter?
A 24V inverter is the ideal balance between simplicity and performance in off-grid installations with medium consumption. By operating at 24 V DC, the current is half that of 12 V for the same power, which reduces losses in the wiring, allows for more reasonable cable sizes, and promotes more efficient system operation.
Advantages of 24V compared to 12V
- Less voltage drop in battery–inverter sections.
- Higher sustained power without extreme currents.
- Cleaner sizing of fuses, disconnectors, and busbars.
And when to move to 48V?
- If the continuous power exceeds ~3 kW or the DC cable runs are long, it is advisable to consider 48V to further reduce the current.
Typical applications
- Off-grid homes with medium consumption (refrigerator, lighting, small appliances, ICT).
- Demanding caravans and campers with several simultaneous loads.
- Small installations in workshops, cabins, and marine applications with higher demand.
Key selection criteria
- Nominal and peak power: calculate simultaneous loads and start-ups (compressors, pumps).
- Pure sine wave to protect electronics and motors.
- Low efficiency losses and standby consumption to save battery.
-
Integrated functions:
- Need to charge from grid/generator? → inverter with 24V charger.
- Need to connect panels directly? → inverter with charger + MPPT or with MPPT.
- Protections (low voltage, overtemperature, short circuit) and communications (RS485/CAN, Wi-Fi/Bluetooth).
- IP rating and ventilation suitable for the environment.
General specifications
| DC input | 24 V (AGM/GEL/Stationary or Lithium 24 V banks) |
| AC output | 230 V single-phase |
| Power range | ~1–4 kW (depending on model) |
| Waveform | Pure sine wave |
| Options | Integrated AC charger, integrated MPPT, source priority, ECO |
Installation best practices
- Install a DC fuse close to the battery positive and an accessible disconnector.
- Use properly sized cables to keep the voltage drop <3% in the DC section.
- Adjust the battery thresholds (type and voltages) and check ventilation and thermal dissipation.
For projects that exceed the typical scope of 12 V but do not require 48 V, 24V inverters offer an efficiency boost with a still simple installation. Also review the options with 24V charger and with integrated MPPT to simplify the system.