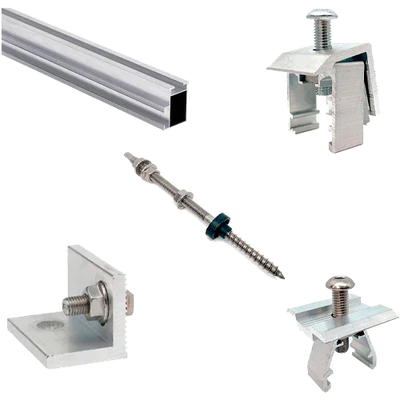
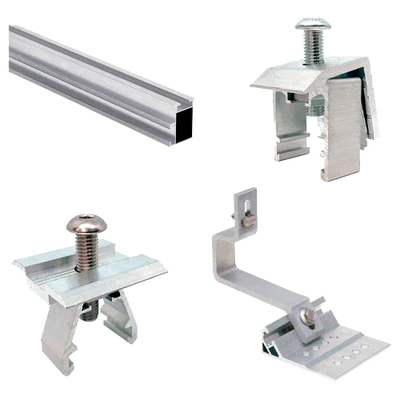
Filter and sort
What are coplanar structures for solar panels?
Coplanar structures are systems of profiles and anchors that allow solar panels to be installed parallel to the plane of a pitched roof. Their purpose is to safely transfer wind and snow loads to the structural support, preserve the watertightness of the roof, and maintain rear ventilation of the module for stable performance. Within the general family of structures for solar panels, coplanar types are the preferred option on pitched roofs due to their aesthetic integration and low aerodynamic impact.
Advantages and limitations
- Discreet integration: by following the slope of the roof, they minimize visual impact and shading.
- Lower wind load: they reduce uplift and stresses compared to inclined racks.
- Fast installation: pre-drilled rails and universal clamps speed up assembly.
- Compatibility: solutions for curved/flat tile, slate, concrete, or fiber cement.
- Limitations: the roof angle determines the tilt of the PV array; if energy optimization is sought, a solution for flat roof or ground may be preferable.
Applications
- Single-family homes and townhouses with gable roofs.
- Commercial buildings with pitched roofs where aesthetics are a priority.
- Renovations where minimal intervention and maximum watertightness are required.
How to choose the right solution
- Type of roof: hooks for tile, through-bolts in concrete/wood, or specific supports for fiber cement.
- Load-bearing structure: locate beams/rafters for anchoring; avoid weak or deteriorated areas.
- Wind zone and height: affect edge spacing and anchor density.
- Module compatibility: frame height (e.g., 30–40 mm) and support spacing according to the technical datasheet.
- Cable management: protected routes, roof penetrations, and UV protection.
Typical specifications
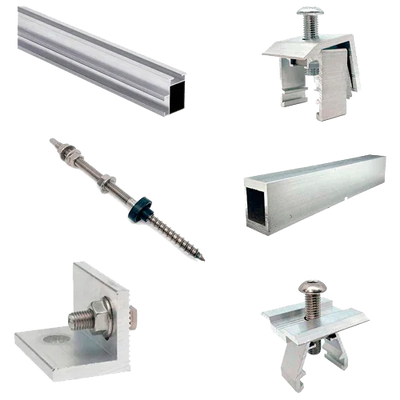
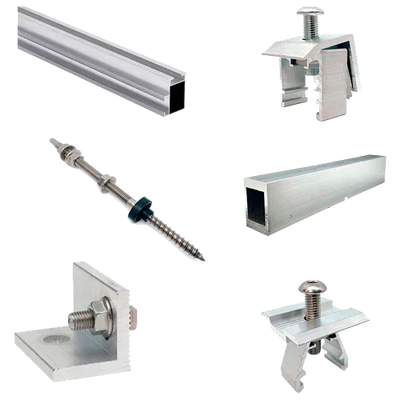
| Materials | Structural aluminium (profiles/clamps) and stainless steel A2/A4 (fasteners) |
| Fixing to roof | Tile hooks, through-bolts, or specific supports with EPDM gaskets |
| Compatible frame height | Approx. 30–40 mm with universal mid and end clamps |
| Design standards | Eurocodes for wind/snow and manufacturer guidelines |
| Protection | Anodized treatments and anti-corrosion fasteners for marine/industrial environments |
| Maintenance | Periodic retightening and inspection of seals and anchor points |
Best practices
- Plan anchor points on a load-bearing structure; do not fix onto tile without transferring load to rafters.
- Use certified flashings and sealants to ensure watertightness.
- Respect tightening torques and edge distances according to wind calculations.
- Ensure rear ventilation of the module and avoid supports on tile edges.
- Route and secure cabling with UV-resistant clamps and anti-abrasion protection.
Quick comparisons
- Coplanar vs flat roof/ground: coplanar prioritizes integration and lower wind load; flat/ground allows optimization of the tilt angle for higher yield.
- Coplanar vs metal roof: for sheet metal, specific fixings with self-drilling screws and EPDM gaskets are recommended.
Related accessories
Complete the installation with compatible clamps, connectors, rails, end caps, and fasteners. For a comprehensive overview of options by support type, see the main collection Structures for Solar Panels.
If your project is not for a pitched roof, explore alternatives: Structures for Ground and Flat Roof or Structures for Metal Roof. With the correct selection and suitable accessories, a coplanar structure offers safety, durability, and a professional finish throughout the entire service life of the PV system.