Filter and sort
What is a structure for solar panels?
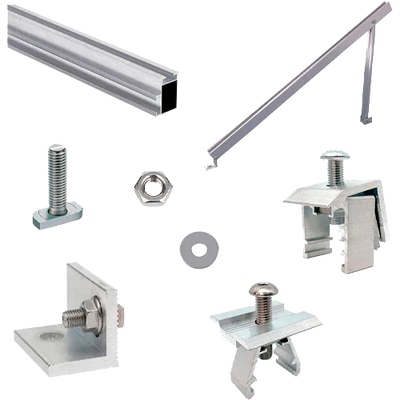
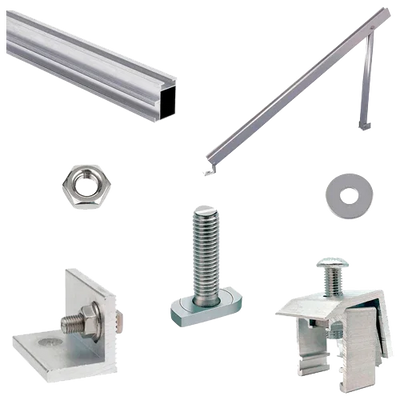
A photovoltaic structure is the set of profiles, joints, and anchors that secures the panel to the support (pitched roof, flat roof, or ground). Its purpose is to transfer wind and snow loads, allow rear ventilation of the module, and maintain the geometry of the PV array safely throughout its entire service life. In this category, we group coplanar solutions, for ground and flat roofs, and for metal roofs, as well as compatible accessories.
Advantages and limitations
- Durability: aluminum profiles and stainless steel fasteners for high corrosion resistance.
- Quick installation: pre-drilled systems and universal clamps reduce installation times.
- Structural safety: designed with wind and snow coefficients according to European standards.
- Flexibility: coplanar options for pitched roofs and configurations with ballast on flat roofs/ground.
- Limitations: incorrect choice of anchor or ballast can compromise watertightness or oversize the weight; therefore, it is essential to select the appropriate subfamily.
Common applications
- Residential and commercial buildings with gable roofs: Coplanar Structures screwed to the slab or tiles using specific hooks.
- Industry, warehouses, and solar carports: racks on flat roofs or ground with orientation and tilt defined by calculation.
- Trapezoidal and sandwich panels: fixings for metal roofs with self-drilling screws and watertight joints.
How to choose the right structure
- Mounting surface: pitched (coplanar), flat (ballast/triangles), or ground (driven/ballasted).
- Exposure: wind zone, building height, and nearby obstacles determine clamps, spacing, and sections.
- Orientation and tilt: in coplanar, integration is prioritized; on flat/ground, production is optimized by varying the angle.
- Module compatibility: frame height and clamp arrangement (rail length, support spacing).
- Watertightness: on pitched roofs, use certified hooks and flashings; on metal sheets, use screws with EPDM washers.
Typical specifications
| Materials | Structural aluminum (profiles, clamps) and stainless steel A2/A4 (fasteners) |
| Finishes | Anodized/cold galvanized depending on the part |
| Compatible substrates | Tile, concrete, gravel/ballast, natural ground, trapezoidal or sandwich panel |
| Tilt range | 0º (coplanar) to 35º on racks for flat roof/ground |
| Design standards | Eurocodes (wind/snow) and technical anchoring guides |
| Module fixing | Intermediate and end clamp, compatible with standard frames (30–40 mm) |
Installation best practices
- Check the building's structural points and seal penetrations with approved systems.
- Respect the recommended tightening torque for clamps and rail–support connections.
- Maintain the required distance from the roof edge according to wind calculations.
- On flat roofs, calculate net ballast (uplift/downforce) and use anti-slip bases.
- Route cabling to avoid edges, using cable glands and UV-resistant materials.
Quick comparisons
- Coplanar vs Flat/Ground: coplanar structures prioritize aesthetics and lower wind impact; flat/ground structures maximize production by adjusting the angle.
- Metal roof vs Traditional roof: on metal, drilling is quick and lightweight; on tile, hooks are required and more attention to watertightness is needed.
Related accessories
Complete your system with clamps, joints, rails, and fasteners compatible with the coplanar and ground/flat roof lines.
Explore each subfamily to find the exact solution for your project: Coplanar Structures, Structures for Ground and Flat Roof, Structures for Metal Roof, and Accessories for Structures.